PHONETICS AND PHONOLOGY
Segmental Aspects
LANGUAGE, SPEECH AND COMMUNICATION
While speech is realised only orally, communication is manifested in the spoken or written form. Moreover, it includes not only verbal, and not only linguistic features, but many other factors that influence the interaction between the sender and the recipient.
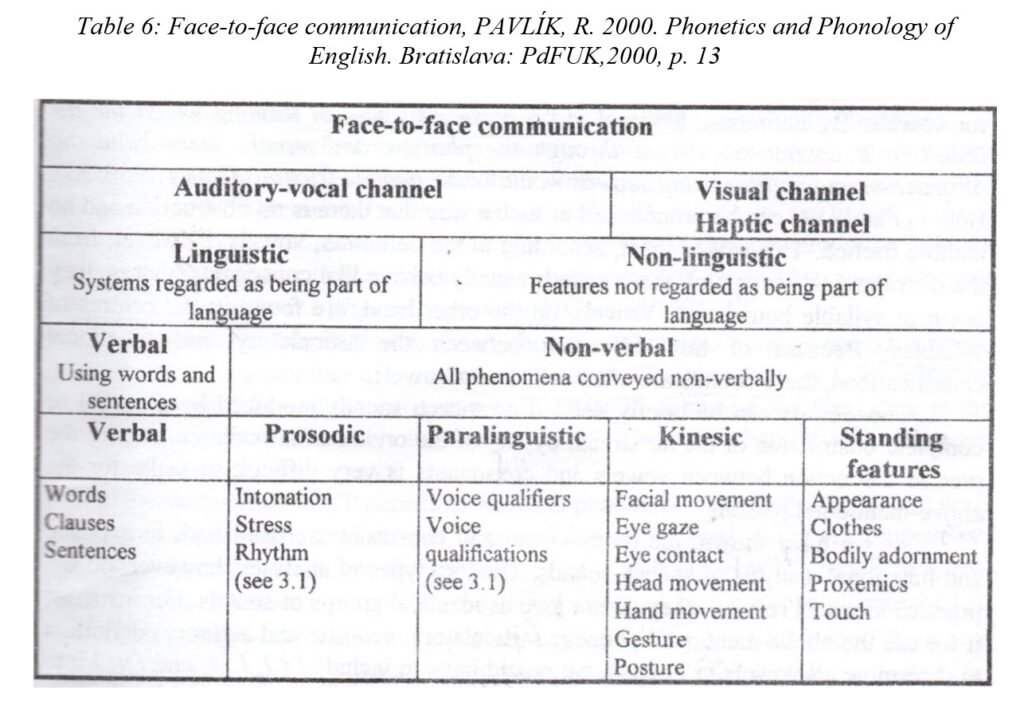
The following Table presented in the publication written by Pavlík (2000) clearly outlines the aspects of face-to-face communication. There are not only verbal and non-verbal aspects included in face-to-face communication, the participants in communication commonly use both linguistic and paralinguistic means: as voice qualifiers, the author mentions qualities of the speaker´s voice which can be “husky, creaky, resonant, guttural”, and “effects as laugh, giggle, sobbing, crying” are understood as voice qualifications (Pavlík, 2000, p. 110).
Human communication is based on combining a limited number of basic elements (phonemes) into higher units (morphemes, syllables, words). This constitutes a system called language. Each language has a finite number of sound elements, and by combining them a person can create an infinite number of sentences (Pavlík, 2019). Štekauer states that “language is conceived as a system of expressive means, and serves for communication. Therefore, it is necessary to investigate the particular functions of language as a system and its components… The spoken and the written forms differ from each other by their peculiarities which must be studied by linguistics” (Štekauer, 1993, p. 105).
Communication is transmission of information. To be able to perform communication, people need to have a channel (in the oral communication, it is air airwaves are spread through) and a code (it is a language – if the participants of communication do not share the same “code”, they will not understand each other, and that will cause breakdown in communication (Pavlík, 2000). Not only the code, but also other aspects of communication are supposed to be in harmony for providing exchange of the information successfully. Purpose for performing communication is influenced by and depends on the partner with whom we communicate. If the sender´s or recipient´s cultural setting correspond, both verbal and non-verbal communication does not have to overcome cultural barriers, but if there is a discrepancy reflected in the process of communication, sharing the same message could be quite problematic (Pondelíková, 2022, p. 97).
Besides general communication performed in the oral or written form, specialised communication is also recognised. The latter type of communication uses specialised terminology of various subject fields. As Cíbiková states in her publication, “terminology is a linguistic and interdisciplinary subject field that deals with designating the concepts and the documentation of knowledge. Terminology has a cognitive, communicative, and sociocultural function” (Cíbiková, 2022, p. 17).
The relationship between language and speech has been discussed and studied by linguists for many decades. It is inevitable to mention at least Ferdinand de Saussure, the representative of Structuralism. He considered language “a general human ability” (Štekauer, 1993, p. 105), and introduced the theory of the opposition of langue and parole based on the idea that langue forms an abstract system, it means “the idealized common knowledge of language functioning perfectly only within a collectivity”, while parole is an act of speaking, it means “the concrete realization of a spoken language (the use of the code by an individual)” (Lančarič, 2008, p. 22). Structuralists emphasized the theory according to which “language is a social phenomenon the main function of which is the communicative function” (Štekauer, 1993, p. 100). Lančarič considers Ferdinand de Saussure “the father of modern structuralist approach to the study of language and the main representative of The Geneva School” (Lančarič, 2008, p. 21).
While discussing the relationship of language and speech, it is also important to mention the nativist approach, represented predominantly by the American linguist Noam Chomsky. The nativist approach “considers people to be biologically endowed with the capability of learning language. That is to say language knowledge develops from the so-called universal grammar, which is a set of principles inherited genetically by all people as an initial idealized stage in language acquisition” (Lančarič, 2008, p. 24). Chomsky differentiates an abstract and a concrete side of every language. He recognises the so-called competence (system and rules of language), and performance (actual use of the rules in the act of speaking).
Language and speech are two interrelated concepts that play a crucial role in human communication. Language refers to the organized, structured way of communicating thoughts, feelings, and ideas through symbols and signs, such as words, grammar, and pronunciation. On the other hand, speech, as a physical manifestation of language, is the act of producing these symbols and signs using voice. All these concepts function as essential components of human interaction, and help to facilitate the exchange of information and the expression of emotions and ideas.

